How to Handle Math Assignments on Cauchy-Euler Equations
Cauchy-Euler equations are a unique class of linear differential equations where the coefficients follow a power-law dependence on the independent variable. Unlike standard linear differential equations with constant coefficients, these equations present additional challenges for students due to their variable-dependent structure. Understanding the theory behind Cauchy-Euler equations is essential for solving them effectively. These equations typically appear in engineering, physics, and applied mathematics, requiring specific techniques to transform them into solvable forms. The key method involves substituting xnx^ terms and reducing the equation to a characteristic equation, similar to solving constant coefficient differential equations. Assignments involving Cauchy-Euler equations can be complex, as they require a strong grasp of both algebraic manipulation and differential equation theory. Recognizing patterns, transforming equations into standard forms, and applying the correct solution techniques are crucial skills. In this blog, we will explore the fundamental concepts of Cauchy-Euler equations, step-by-step solution methods, and practical strategies to handle assignments efficiently. By mastering these techniques, students can confidently solve their math assignment and strengthen their understanding of differential equations. Whether you are new to this topic or looking to refine your approach, this guide will provide valuable insights for tackling Cauchy-Euler equation assignments.

Understanding Cauchy-Euler Equations
A Cauchy-Euler equation is generally of the form:
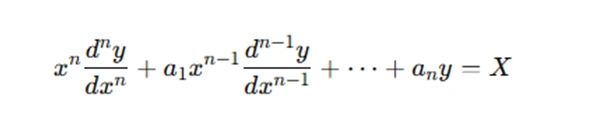
Here, the coefficients a1,a2,…,ana are constants, but the powers of x in each term are different. This non-constant coefficient structure is what makes the equation challenging. Unlike linear differential equations with constant coefficients, where the solution process is more straightforward, Cauchy-Euler equations require a special transformation to convert them into a more solvable form.
Key Challenges in Solving Cauchy-Euler Equations
The key difficulty in solving Cauchy-Euler equations lies in the presence of variable coefficients, which complicates the solution process. In traditional linear differential equations with constant coefficients, methods like the characteristic equation are effective. However, with the Cauchy-Euler equation, the solution is not immediately apparent due to the presence of powers of x in the coefficients. This introduces a layer of complexity that students must navigate carefully in their assignments.
Another challenge is the need to transform the equation into a more manageable form. This often involves using substitutions that convert the Cauchy-Euler equation into an equation with constant coefficients, which can be solved using known methods for linear equations with constant coefficients.
Substituting to Simplify the Cauchy-Euler Equation
To simplify the Cauchy-Euler equation, we use a substitution method. We replace the independent variable x with z=ln), where ln(x) is the natural logarithm of x. This substitution transforms the differential equation into one that is easier to handle.
Derivative Transformation
Once we make this substitution, we need to express the derivatives in terms of the new variable z. The first step is to compute the derivative of y with respect to x. Using the chain rule, we have:
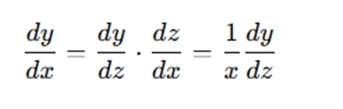
For higher-order derivatives, the transformation becomes more involved. For example, the second derivative transforms as follows:
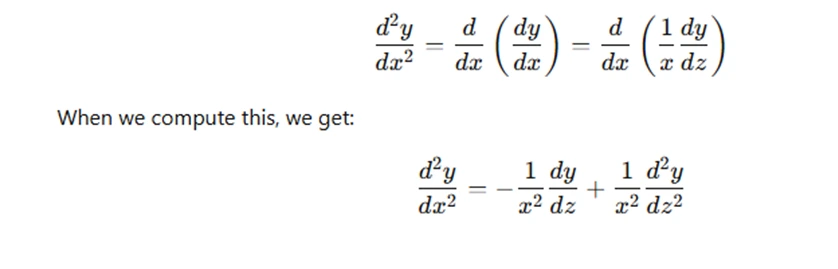
In this way, the higher-order derivatives are expressed in terms of derivatives with respect to z. This conversion allows us to simplify the Cauchy-Euler equation into a linear equation with constant coefficients.
Transforming the Cauchy-Euler Equation
The transformation of the equation into a linear equation with constant coefficients can be summarized as follows:
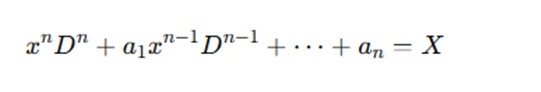
After substituting z=ln(x) the equation is transformed into a form with constant coefficients, which can be solved using traditional methods for solving linear differential equations with constant coefficients.
The key advantage of this transformation is that the new equation is easier to solve because the coefficients no longer depend on x, but rather on constants. This transformation is a crucial step in solving the Cauchy-Euler equation, and it is often the first task when faced with such an equation in an assignment.
General Solution to the Cauchy-Euler Equation
Once the Cauchy-Euler equation has been transformed into a linear equation with constant coefficients, the next step is to find the general solution. The general solution consists of two parts: the complementary function and the particular integral.
Complementary Function
The complementary function, denoted as ycy_cyc, is the solution to the homogeneous equation (where the right-hand side is set to zero). For the Cauchy-Euler equation, the complementary function typically takes the form:
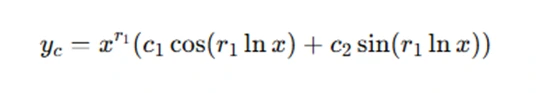
Here, r1 is a constant that is determined by solving the characteristic equation associated with the transformed equation. This part of the solution represents the general form of the solution to the homogeneous equation.
Particular Integral
The particular integral, denoted as ypy , is the solution to the non-homogeneous equation (where the right-hand side is not zero). To find the particular integral, we use a method such as undetermined coefficients or variation of parameters. The particular integral is tailored to the form of the non-homogeneous term on the right-hand side of the equation.
Once both the complementary function and the particular integral are found, the general solution to the Cauchy-Euler equation is given by:
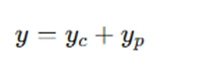
This general solution can then be used to solve specific problems in assignments by substituting initial conditions or boundary conditions to determine the values of the constants c1 and c2.
Example of Solving a Cauchy-Euler Equation
Let us consider a simple example to demonstrate the solution process. Suppose we have the following Cauchy-Euler equation:
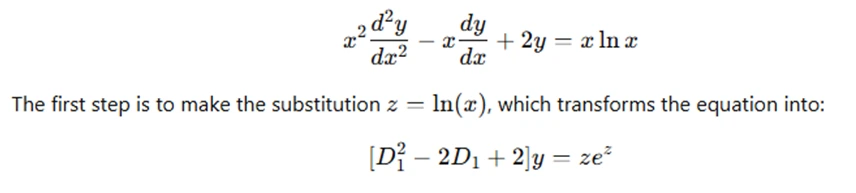
Here, D1 denotes the derivative with respect to z. The equation is now a linear equation with constant coefficients, which can be solved using standard methods for second-order linear differential equations.
The complementary function is found by solving the homogeneous equation:
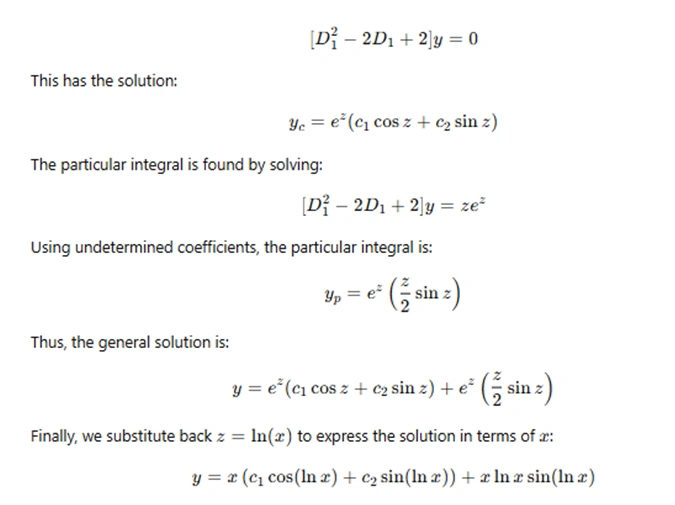
This is the general solution to the Cauchy-Euler equation. By applying initial conditions or boundary conditions, we can determine the values of the constants c1 and c2.
Tips for Tackling Cauchy-Euler Equations in Assignments
Here are some practical tips to help you handle Cauchy-Euler equations in your assignments:
- Understand the Transformation: The substitution z=ln(x) is crucial. Make sure you fully understand how it simplifies the equation and how to handle the derivatives after the substitution.
- Solve the Characteristic Equation: The characteristic equation for the homogeneous part of the equation is a key step. Be sure to solve it correctly to find the complementary function.
- Use Standard Methods: Once the equation is reduced to one with constant coefficients, use standard methods for solving linear differential equations, such as undetermined coefficients or variation of parameters, to find the particular integral.
- Pay Attention to the Particular Integral: The particular integral is tailored to the right-hand side of the equation. Ensure that you correctly handle non-homogeneous terms like xln in the example above.
- Check Your Work: After obtaining a solution, always substitute it back into the original equation to verify that it satisfies the equation.
Conclusion
The Cauchy-Euler equation is a crucial topic in differential equations that students often encounter in their academic journey. Understanding its theoretical foundation and mastering the solution techniques can help students solve complex mathematical problems with confidence. This type of equation is commonly used in engineering, physics, and applied mathematics, making it essential for students to develop strong problem-solving skills in this area. The solution process involves transforming the equation into a more manageable form, solving the characteristic equation, and finding the general solution. Each step enhances a student’s understanding of linear differential equations and provides valuable practice in analytical thinking. By carefully following a structured approach, students can efficiently handle Cauchy-Euler equations, whether in coursework, exams, or real-world applications. Developing proficiency in these techniques ensures a solid mathematical foundation and better performance in assignments. With dedication and practice, mastering Cauchy-Euler equations becomes an achievable goal, empowering students to tackle advanced problems in their studies and future careers.