Efficient Way to Solve Math Assignment on Linear Transformations

Linear transformations, also known as linear maps, are fundamental concepts in mathematics, particularly in linear algebra and vector spaces. These transformations preserve vector addition and scalar multiplication, making them essential in various mathematical applications. University students often encounter linear transformations in assignments, where they analyze functions that map one vector space to another while maintaining linearity. Studying linear transformations requires a deep understanding of their properties, such as additivity and homogeneity. These properties ensure that operations within the vector space remain consistent under transformation. Additionally, matrix representations of linear transformations help simplify complex problems, making it easier to visualize and compute transformations efficiently. Assignments on linear transformations often involve verifying linearity, finding the kernel and range, and applying transformations to solve real-world problems. Students may face challenges in understanding higher-dimensional transformations, matrix computations, and abstract vector space mappings. Overcoming these difficulties requires systematic practice, conceptual visualization, and problem-solving techniques. By mastering linear transformations, students gain valuable analytical skills applicable in physics, computer graphics, and engineering. A strong foundation in this topic enhances problem-solving abilities, enabling students to solve their math assignment with confidence. Understanding and applying linear transformations effectively will significantly improve mathematical proficiency and academic success.

What Are Linear Transformations?
A linear transformation is a mapping between two vector spaces, often denoted as F:X→Y, where X and Y are vector spaces. The transformation F is called linear if it satisfies two key properties:
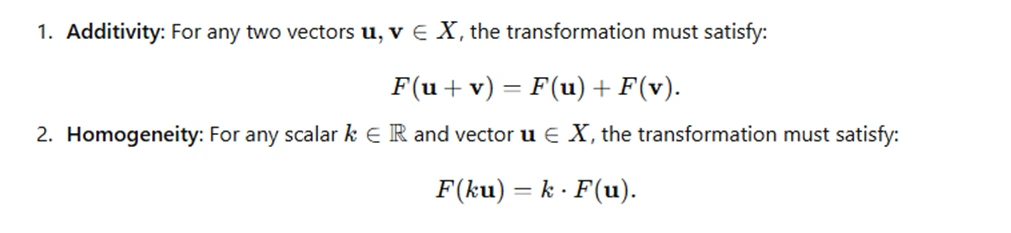
These two properties ensure that the transformation preserves the structure of vector spaces, making it a linear operation. By satisfying these conditions, linear transformations can map vectors from one space to another while maintaining their linear properties.
The Key Properties of Linear Transformations
In addition to additivity and homogeneity, linear transformations have some fundamental characteristics that make them unique and easy to work with. Here are a few essential properties:
- Zero Vector Mapping: One key property of linear transformations is that they map the zero vector in the domain X to the zero vector in the codomain Y. That is, F(0)=0. This is a necessary condition for linearity and helps ensure the consistency of the transformation.
- Commutativity of Scalars: When dealing with scalar multiplication, a linear transformation will distribute over scalars. Specifically, F(k1u+k2v)=k1 F(u)+k2F(v) This feature allows linear transformations to maintain proportionality across transformations.
- Composition of Linear Transformations: If two transformations FFF and GGG are linear, then their composition F∘GF \circ GF∘G is also a linear transformation. This property is vital in many applications, as it allows the combination of various linear operations into one.
How to Study Linear Transformations
Studying linear transformations can be daunting, but with a structured approach, the process becomes manageable. Here's how you can effectively study and apply linear transformations, especially in your assignments:
- Understand the Core Properties: Start by focusing on the two fundamental properties of linear transformations: additivity and homogeneity. Understanding these properties will help you identify whether a given transformation is linear.
- Visualize the Concept: One of the most challenging aspects of linear transformations is conceptualizing how they act on vectors. Visual aids like diagrams can help you visualize how transformations map vectors from one space to another. For example, in the transformation F:R3→R3 defined by F(x,y,z)=(x,y,0), the transformation projects a 3D vector onto the xy-plane. Understanding these geometric interpretations will aid you in applying the concept to more complex assignments.
- Work Through Examples: The best way to reinforce your understanding is through practice. Start by solving simple problems where you check whether a given transformation is linear by verifying the two conditions (additivity and homogeneity). Gradually work your way up to more complex problems involving matrix representations of linear transformations.
- Study Matrix Representation: In many cases, linear transformations can be represented by matrices. Understanding how a matrix represents a linear transformation will help you translate between abstract vector space operations and concrete matrix calculations. Learning how to multiply matrices and apply transformations using matrices will streamline your problem-solving process.
- Apply Transformations in Context: Linear transformations are used in various contexts, including computer graphics, data analysis, and systems of equations. In assignments, you may encounter real-world problems where linear transformations model processes such as scaling, rotating, or translating objects. Apply the theoretical knowledge to these contexts to gain a deeper understanding
Common Challenges in Solving Linear Transformation Problems
While studying linear transformations is essential, many students face challenges when solving related assignments. Here are some common hurdles and how to overcome them:
- Identifying Whether a Transformation is Linear: One of the first challenges students face is determining whether a given transformation is linear. To do this, carefully check the two core properties: additivity and homogeneity. If either of these properties is violated, the transformation is not linear. Pay close attention to transformations that involve shifting or translating vectors, as these are often not linear.
- Dealing with Nonlinear Transformations: Not all transformations are linear. For example, a transformation that shifts every vector by a constant is not linear because it does not satisfy the condition F(0)=0. In such cases, recognize the transformation's nature and approach the problem accordingly, focusing on understanding the underlying principles behind the transformation.
- Working with Matrices: When linear transformations are represented by matrices, students often struggle with matrix multiplication and applying the transformation to vectors. To overcome this, review matrix multiplication rules and practice applying transformations using matrices. Ensure that you understand how matrix-vector multiplication works, and don't hesitate to ask for help if you're unsure about matrix operations.
- Understanding the Kernel and Range: The kernel of a linear transformation refers to the set of vectors in the domain that are mapped to the zero vector in the codomain. The range refers to the set of all possible outputs in the codomain. Understanding the kernel and range is critical in solving linear transformation problems, particularly when determining whether a transformation is invertible or analyzing its properties. Focus on these concepts by solving problems that involve finding the kernel and range.
- Dealing with Multiple Dimensions: Linear transformations often involve vector spaces of multiple dimensions, such as Rn. Understanding how transformations operate in higher-dimensional spaces can be challenging. To tackle this, practice solving problems in both low-dimensional and high-dimensional spaces to develop an intuition for how transformations behave in different contexts.
- Verifying Linearity with Specific Examples: A key challenge when solving linear transformation problems is verifying whether a given transformation satisfies the linearity conditions. Take the time to work through specific examples step by step. For example, in the transformation F:R2→R2 defined by F(x,y)=(x+1,y+2), check if the transformation satisfies the linearity conditions by substituting specific vectors and scalars. In this case, the transformation does not map the zero vector to the zero vector, and thus it is not linear.
- Applying Transformations to Complex Systems: Many problems involving linear transformations come from real-world scenarios, such as systems of linear equations or geometric transformations. Understanding how linear transformations apply to these complex systems can be difficult. To excel in these types of problems, break them down into smaller parts, focusing on one transformation at a time, and apply the theoretical concepts to the practical situation.
Conclusion
Mastering linear transformations requires a solid understanding of the core properties, the ability to recognize and apply these properties in various contexts, and practice solving problems. Throughout your studies, it's important to approach linear transformation problems methodically, breaking them down into manageable parts and reinforcing your understanding with hands-on examples.
When working on assignments, remember that linear transformations are a powerful tool in mathematics that preserves the structure of vector spaces. By developing a strong conceptual foundation, working through practice problems, and learning to apply these concepts to real-world situations, you'll be well-equipped to tackle any linear transformation problems that come your way. With patience and practice, the challenges you encounter along the way will become stepping stones to success in mastering this crucial topic.